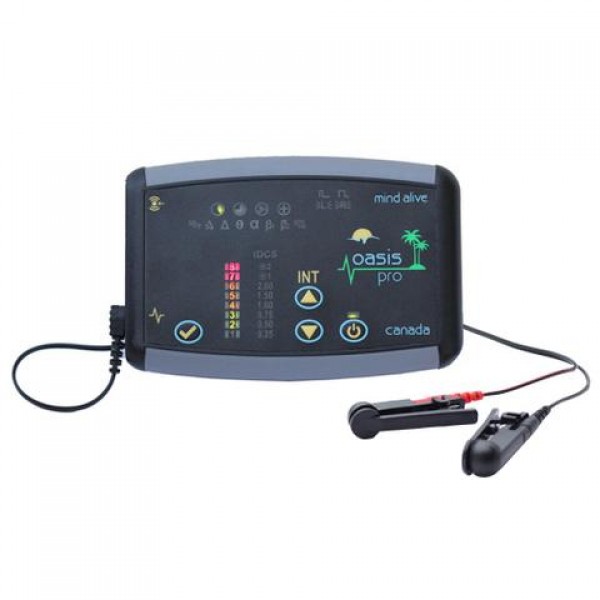
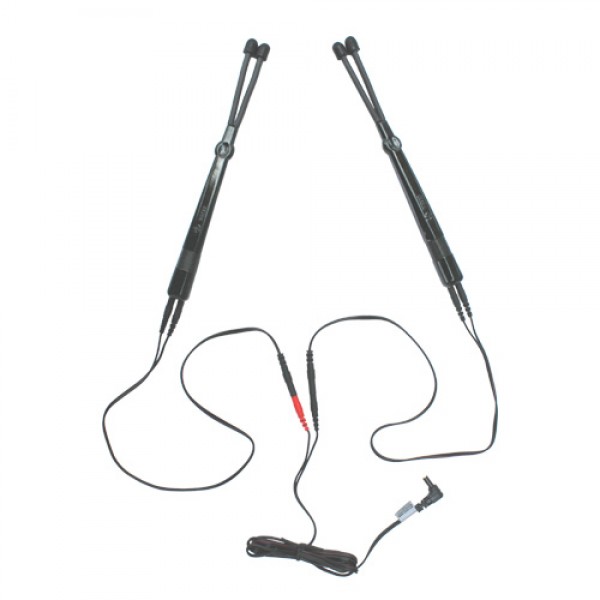
Mind Alive OASIS Pro
EACH OASIS PRO COMES COMPLETE WITH:
Stimulus Cable with Earclips
Carry case
9-Volt Alkaline Battery
Comprehensive Operator's Manual
This product runs on battery power only. (no AC Adapter required)
Additional features include:
User Programmable with optional DAVID Session Editor CD
Randomization
50 % Duty Cycle Sub-Delta session
MET (optional)
tDCS (optional)
About Cranio-Electro Stimulation (CES)
Cranio-Electro Stimulation (CES) was developed in the Soviet Union in the late 1940s as a treatment for insomnia and has since been used by millions of people all over the world.
Over 200 studies to date have shown that CES increase the calming type of neurotransmitters within the brain, namely serotonin and endorphins. Clinical research over the past 50 years has shown that CES calms the mind, boosts relaxation, helps with sleep and improves mental sharpness and ability in general. CES is particularly useful in producing calm in situations like being at the dentist, while writing exams or struggling with the fast pace of work or school. CES also settles body discomfort.
About Microcurrent Electro Therapy (MET)
Although electro-medicine has been in existence for well over a thousand years, developments in electronics and new research has seen this technology grow at a terrific rate in recent years. Microcurrent Electro Therapy (MET) is very different than traditional TENS because MET produces its benefits in part on a cellular level. MET has longer lasting effects than TENS.
The concept of MET is based, in part, on Arndt’s Law, which states that weak stimuli excite physiological activity, whereas medium-strength stimuli will encourage it and strong stimuli will suppress it.
It is believed that MET delivered at around 500 micro-amps in the 0.5 to 3 Hz range may be most effective for treating pain.
About Transcranial DC Stimulation (tDCS)
When a DC current is applied over the scalp with the intention of altering neuronal activity, it is known as transcranial DC stimulation. tDCS is effective in modulating spontaneous neuronal firing. tDCS at intensities of 1 milliamp applied for roughly 20 minutes has been shown to either excite or inhibit the sensori-motor cortex, with the effects lasting over an hour. Excitation is achieved by anodal (+) stimulation, while inhibition is achieved by cathodal (-) stimulation. Anodal stimulation has also been shown to increase both beta and gamma activity in the visual cortex, while cathodal stimulation has decreased beta and gamma activity. Stimulation is generated by putting a wet cloth, cotton ball or sponge on the scalp over the brain region to be treated and a sponge or cotton ball on the shoulder or the face. The tDCS sessions deliver a maximum intensity of 2.2 milliamps at DC. tDCS is being used for the treatment of many conditions, including depression.